Authors:
Ryan Rocke, Lili Zhang
MIT Supply Chain Management Program
72
Summary:
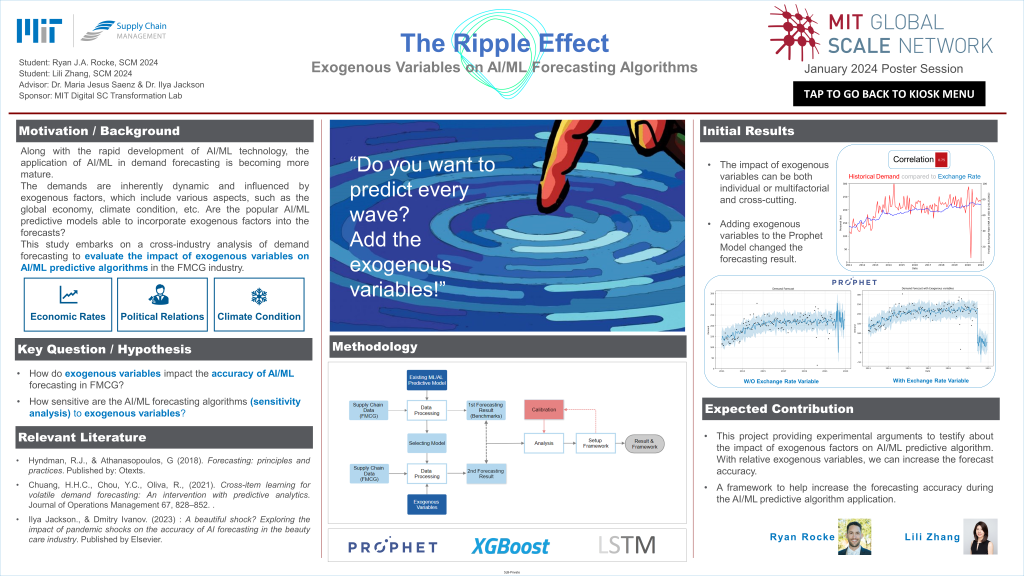
As we transition through the “Fourth Industrial Revolution” (K. Schwab, 2017), organizations increasingly leverage AI and ML for rapid, data-driven decision-making, however, still face the risk of supply chain disruption influenced by external (exogenous) events. This study embarks on a cross-industry analysis of demand forecasting to evaluate the impact of exogenous variables—specifically economic rates, political relations, and climate conditions—on AI/ML predictive algorithms in fast-moving consumer goods. Through a rigorous methodology employing models such as Prophet, Random Forest, and LSTM, the research aims to enhance the robustness of demand predictions, offering strategic insights to businesses for integrating external variables into their forecasting models, thereby improving efficiency and competitiveness in a dynamic global market.


Bravo